Thermogravimetric Thermal Analysis (TGA)

Westmoreland Mechanical Testing & Research provides Thermalgravimetric Analysis (TGA) to measure mass of a sample over time as the temperature changes.
This measurement, provides information about phase transitions, absorption and desorption; as well as chemisorptions, thermal decomposition, and solid-gas reactions. TGA is useful for the study of polymeric materials, including thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, composites, plastic films, fibers, coatings, paints, and fuels.”
Expedited Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) Services Are Available- Contact Us Today at 724-537-3131
- Accreditations: NADCAP since 1992, A2LA (A2LA for DSC portion)
and ISO 17025 - Also referred to as STA (Simultaneous Thermal Analysis)
- Measures mass and enthalpic change over a given temperature profile
- Capable of temperature range of RT to 3000ºF
- XP5 balance: Capable of samples up to 5 grams (1.0 ug resolution)
- Gas Controller to allow for inert and reactive gas atmosphere
What Is Thermogravimetric Used For?
The Thermogravimetric Analyzer (TGA) measures the change in weight of a sample as tested through a temperature profile. The TGA can provide information about chemical phenomena including chemisorptions, desolvation and dehydration, decomposition, and solid-gas reactions such as oxidation or reduction.
A Thermogravimetric Thermal Analysis (TGA) is performed by gradually raising the temperature of a sample in a furnace as its weight is measured on an analytical balance that remains outside of the furnace. In TGA, mass loss is observed if a thermal event involves loss of a volatile component.
TGA/DSC
.jpg)
The Following Graph Represents Plotting for Sample Mass vs. Temperature Test: Decomposition/ Thermal Stability
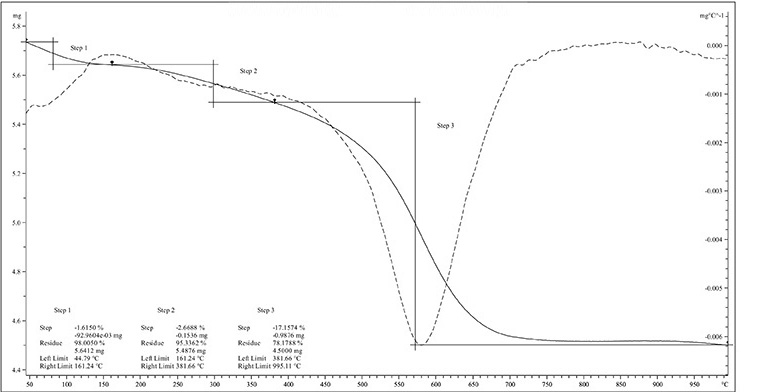
Thermogravimetric Thermal Analysis (TGA) can be used for materials characterization through analysis of characteristic decomposition patterns. It is an especially useful technique for the study of thermoplastics, thermosets, elastomers, composites, plastic films, fibers, adhesives, coatings, paints, and fuels.
Thermogravimetric Thermal Analysis (TGA) Standardized Tests
ASTM D3850
Standard Test Method for Rapid Thermal Degradation of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials by Thermogravimetric (TGA) Method
Test Method
This thermogravimetric technique uses the record of the mass loss versus the temperature of the specimen during the time of exposure to a specified prescribed environment using a controlled time rate of heating.
Test Specimen
Specimens of 2 to 20 mg are satisfactory, depending on the configuration. Test results depend in part on the size and shape of specimen, due to thermal equilibrium and diffusion effects.
Significance and Use
Thermogravimetry is useful in determining the dynamic functional effect of temperature on the amount of volatile materials leaving a specimen as the latter is heated progressively to higher temperatures. Thermogravimetric Thermal Analysis (TGA) can be useful for process control, process development, material evaluation, and for identification and quality control in specifications.
The thermal stability of a material can be associated with the degree and time rate of mass loss as a function of temperature. TGA curves can, therefore, be used as a preliminary screen method in the evaluation of relative behavior of insulating materials of the same generic family.
Need more
Information on Thermogravimetric Thermal Analysis (TGA)? -
Contact Us Today at 724-537-3131
ASTM E1131
Standard Test Method for Compositional Analysis by Thermogravimetry
Test Method
This thermogravimetric technique uses the record of the mass loss versus the temperature of the specimen during the time of exposure to a specified prescribed environment using a controlled time rate of heating.
Test Specimen
Specimens of 2 to 20 mg are satisfactory, depending on the configuration. Test results depend in part on the size and shape of specimen, due to thermal equilibrium and diffusion effects.
Significance and Use
Thermogravimetry is useful in determining the dynamic functional effect of temperature on the amount of volatile materials leaving a specimen as the latter is heated progressively to higher temperatures. Thermogravimetric Thermal Analysis (TGA) can be useful for process control, process development, material evaluation, and for identification and quality control in specifications.
The thermal stability of a material can be associated with the degree and time rate of mass loss as a function of temperature. Thermogravimetric Thermal Analysis (TGA) curves can, therefore, be used as a preliminary screen method in the evaluation of relative behavior of insulating materials of the same generic family.
ASTM E2550
Standard Test Method for Thermal Stability by Thermogravimetry
Test Method
A sample of the material to be examined is placed in an inert container and then heated at a controlled rate (β) of 1°C min-1 to 20°C min-1 under a controlled atmosphere. The sample mass is recorded continuously as a function of time and temperature. When the sample undergoes a reaction or thermal decomposition involving a mass change, that change is indicated by a departure from the initially established baseline of the mass record.
Test Specimen
The selection of specimen mass depends upon the magnitude of hazard associated with the material, the sensitivity of the instrument, the heating rate and the specimen homogeneity. This test method should be carried out on as small of a quantity of material as possible, while specimens are still large enough to be representative of the material and to exhibit adequate signals. Typical specimen mass is between 1 mg and 10 mg.>.
Significance of Use
Thermogravimetry provides a rapid method for determining the thermal decomposition and reaction mass change of a material.
This test method is useful in detecting potentially hazardous reactions and in estimating the temperatures at which these reactions occur. This test method is recommended as a screening test for detecting the thermal hazards of an uncharacterized material or mixture.
Energetic materials, pharmaceuticals and polymers are examples of materials for which this test might be useful. This test is especially useful for materials having melting points that overlap with the onset of reaction or decomposition.



